——A governance-based perspective
China.com/China Development Portal News Our country is promoting a modern national governance system. As the main body of the natural protected area system and an important area for promoting the construction of ecological civilization system, national parks need to take the lead in Zelanian sugar and break through traditional administration Constraints of the management and control model, explore the path to construct a modernized governance system for China’s national parks.
National parks combine nature, geography, humanities, history and other elements, and are a complex of multiple functions such as ecological protection, scientific research, natural education, ecological experience, and green development. In the face of complex governance elements and diverse stakeholders, the importance of scientific decision-making in national parks is extremely prominent, and an effective consultation mechanism is an important guarantee for improving the scientific nature of decision-making and improving the effectiveness of governance. Since the pilot of the national park system, my country’s competent authorities have carried out many explorations of scientific decision-making and consultation. However, the standardization of relevant work and the perfection of supporting systems are still insufficient, and there is an urgent need for systematic research and demonstration. This study is problem-oriented, fully draws on international experience, and discusses the key elements of the establishment of scientific decision-making and consultation mechanisms for national parks in my country from the perspective of governance. It attempts to answer how to establish the organizational form of scientific decision-making and consultation for national parks from the perspective of governance. and the positioning of powers and responsibilities of consulting agencies.
Decision-making and consultation in national park governance
The complexity of national park governance
Governance It is a concept that is different from administrative control. It has the characteristics of diversification of subjects, dynamics and adaptability of the process, and emphasizes the distribution of rights and responsibilities and the sharing of interests among multiple parties. The governance of national parks is highly complex. Guided by the three concepts of ecological protection first, national representativeness, and public welfare, the national park takes the integrity and authenticity of important ecosystems as its protection goals, and takes the harmonious coexistence of man and nature as its vision. It also has scientific research, Functions such as nature education, ecological experience, and green development are a multi-element, multi-functional, and multi-dimensional complex.
The complex natural attributes and the relationship between man and land further increase the difficulty of national park management. NZ Escorts The ecological environment itself has multi-dimensional, dynamic, complex and other characteristics, such as: professionalism stemming from the uncertainty of biodiversity and environmental factors characteristics, regional differences caused by differences in land space and natural conditions, systematic characteristics resulting from the mutual integration of various ecological environment elements and biodiversity elements through ecological processes such as energy flow and material circulation. With the goal of protecting ecosystem integrity, national parks involve diverse ecological elements and spatial structure elements.The complex industrial and regional relationships, coupled with the vision and goal of harmonious coexistence between man and nature, make national parks have a larger and more complex stakeholder network than other spatial entities. In addition, my country’s huge population base, long history of symbiosis between man and land, and the coexistence of natural resources owned by the whole people and collectively owned have increased the complexity of governance to varying degrees.
The necessity of establishing a scientific decision-making and consultation mechanism for national parks
Decision-making is the prerequisite for the development of various undertakings, and the governance of complex systems requires scientific and democratic decision making. A reasonable and efficient scientific decision-making and consultation mechanism is an important foundation for effectively coordinating the three-way interaction between the public sector, social forces, and the private sector and ensuring the publicity and serviceability of public governance. It is one of the key paths for effective governance of complex systems.
The decision-making of national park management must be the optimal choice to fully utilize the multiple functions of the national park under the premise of ecological protection. It must be a “no-regret choice” that will not cause irreversible effects on the ecosystem and be able to A wise choice that takes into account the interests of the vast majority of groups. By establishing a scientific decision-making and consultation mechanism, we can fully recruit scientific groups and industry representatives to provide consulting services and support decision-making and implementation, fully leverage the advantages of collective intelligence, coordinate the relationship between different stakeholders, drive social participation, and coordinate social economy and resource allocation. It is a necessary step to avoid the path deviation under the government’s “authoritarian” management and gradually guide decision-making power from class privileges to public power based on scientific facts and the objective needs of social development.
Problems and roots of the national park decision-making system
The construction of my country’s national parks is a process of “breaking and building at the same time”. At the beginning of the system pilot, the National Development and Reform Commission took the lead and collaborated with 12 ministries and commissions to carry out a series of decision-making consultation work, including establishing a multi-disciplinary core expert group and relying on scientific groups to promote documents such as the “Overall Plan for Establishing a National Park System” The introduction of etc. After the institutional reorganization of the State Council in 2018, under the comprehensive coordination of the newly established National Forestry and Grassland Administration, the coverage of national park decision-making consultation work has gradually expanded. For example, research and consulting institutions at different levels have been gradually established, and national public institutionsSugar DaddyGarden establishmentZelanian Escortlaw and planning, acceptance evaluation, etc. The work has attracted scientific research institutions such as the Chinese Academy of Sciences as technical support and decision-making consulting departments.
Scientific decision-making and consultation work in national parks has made significant progress, but problems cannot be ignored. Through interviews and questionnaire surveys with representatives of legislative bodies, experts and scholars, frontline management and staff representatives, and community residents, the author found that there are decision-making deficiencies in many aspects of national park governance.Although it is related to the fact that the opinions and suggestions of scientific groups and representatives from all walks of life have not been fully and reasonably reflected, the fundamental reason lies in the imperfect system and imperfect mechanism.
Specific manifestations of deficiencies in decision-making in national park governance
National park governance involves the establishment of rules and regulations, planning and layout, protection and restoration, public services, community development, etc. Affairs, the decision-making flaws in each link are concentrated in four aspects.
The evaluation and demonstration of some major decisions such as selection and establishment are insufficient. The national representativeness, ecological importance and management feasibility have not yet been fully demonstrated, and the natural resource assets integrated management plan and management system Before the mechanism is clear, the situation of rebuilding light pipes and pursuing quantity and speed still exists.
The disciplinary support on which decision-making relies is not comprehensive enoughZelanian Escort. Ecology, forestry and other related majors occupy a mainstream position in national park planning and management. Experts in management, sociology, economics, law and other fields are insufficiently involved, and the subject coverage is still relatively narrow.
Community rights and interests are not fully protected. Affected by the traditional management model of nature reserves, the compatible development path between national parks and communities has not yet been clearly defined. Resettlement and relocation, logging banZelanian Escortgrazing ban Such “one size fits all” policies have triggered negative emotions among community residents to a certain extent.
The paths and methods for the participation of social forces are not clear. The willingness of community groups such as social organizations, enterprises and individuals to express their demands, make suggestions and even support decision-making consultations is increasing. However, the channels for participation are relatively single, the methods are not clear enough, and the level of participation is insufficient.
The fundamental reasons at the system and mechanism level
Insufficient systems and mechanisms are one of the fundamental reasons for the defects in national park governance decision-making, which are specifically reflected in 4 aspects.
The positioning of rights and responsibilities is vague, and the independent third-party support role of consulting agencies is not significant. In recent years, various national park research institutes, expert committees and other technical support and decision-making advisory bodies have emerged rapidly from the state to the local level, but their functional positioning is not clear enough – which tasks require expert consultation, scientific groups and other advisory bodies have different roles. There is currently no clear institutional plan for what rights and responsibilities there are for affairs, what forms and paths are available for consultation, etc. This results in the transfer of independent argumentation, neutral advice and other rights of consulting agencies to decision-makers, affecting the objectivity and effectiveness of consultation. .
The path dependence of departmental management has not yet been broken through, and there are still departmental barriers to decision-making consultation. byDue to the long-term influence of industrialized management of natural protected areas, the decision-making consulting services of national parks are now mainly focused on the natural science fields, mainly forestry and ecology. The composition of experts, consulting services, consulting processes and decision-making models are still comprehensive in disciplines. Not prominent enough.
The linkage mechanism between decision-making and scientific research is not sound enough, and scientific research results have not effectively played a role in decision-making support. The functions of decision-making departments and advisory bodies Sugar Daddy are different. The current incentive mechanism for transforming scientific research into decision-making is imperfect; in addition to the national level, many national parks Research institutes or expert committees fail to timely and fully convert scientific research results into effective information required for decision-making, and the decision-making support role of scientific research is not significant enough.
The institutional constraints of decision-making consultation are insufficient, the procedures are not standardized enough, and the effectiveness of consultation is not significant enough. Our country has not yet introduced a special system for the work scope, organizational form and operating procedures of national park decision-making consultation. Not only the staffing and funding of consulting agencies cannot be included in normal management, but also problems such as limitations, randomness and temporary nature of consultation work occur from time to time. , and some consultation arguments are merely formal, affecting their rationality and effectiveness.
International experience in scientific decision-making and consultation in national parks
Definition of powers and responsibilities of consulting agencies, multi-disciplinary coordination of consulting experts, and linkage between decision-making and consulting departments Institutional norms for coordination and decision-making consultation are effective means to make up for the shortcomings of national park governance decision-making, but our country currently lacks sufficient practice Newzealand Sugar Experience accumulation. Considering that the operation mode of the advisory mechanism is inseparable from the governance system and Zelanian sugar decision-making mechanism, national parks in the United States and France are centralized management and pluralistic Co-governance is a typical representative of the two governance models, and the corresponding decision-making and consultation mechanisms are also completely different. This study focuses on the cases of these two countries to gain insight into the effective decision-making consultation model for the governance process of public goods owned by the whole people and complex ownership of natural resources, and to provide reference for the governance of China’s national parks that have these characteristics.
The organizational form of national park decision-making consultation in the United States and France
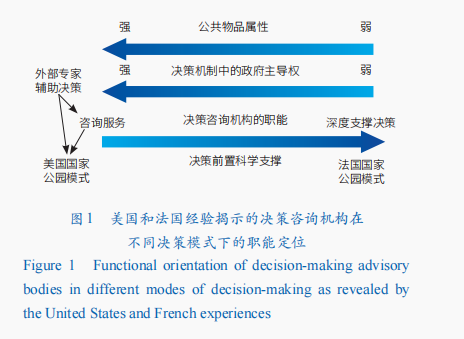
The American model: government-led decision-making, assisted by scientific consultation. The federal land area of the U.S. National Park System accounts for 96%. It is a typical public good owned by the whole people. It implements a government-led decision-making model and is operated by the National Park Service of the U.S. Department of the InteriorNZ Escorts shall exercise its sole discretionPolicy power. As needed, the federal government establishes internal advisory committees with specific functions in accordance with the law, and collaborates with external experts to provide advisory services for national park decision-making. It also forms a check and balance on government decision-making to avoid government monopoly.
French model: pluralistic co-governance, scientific groups exercise decision-making power on major affairs. The land ownership of French national parks is complex, and multiple factors such as environment, culture and economy are intertwined. It takes biodiversity protection and sustainable development as parallel goals and implements multi-faceted co-governance. The French Ministry of Ecological Transformation and Territorial Solidarity is responsible for the overall management of national parks at the national level in accordance with the law. Each national park is jointly governed by a board of directors, a management committee, a scientific expert committee and an economic, social and cultural committee. In addition, the central and various national parks also have chief scientists responsible for decision-making consultation.
The operation model of national park decision-making consultation in the United States and France
The operation model of national park decision-making consultation is matched with the organizational form, which is to a large extent determines the operating mode.
The boundaries of the decision-making advisory body’s powers. Under the single-decision-making system of the federal government in the United States, the advisory bodies of American national parks mainly play the role of assisting decision-making and avoiding the government’s autocratic power. The Federal Advisory Committee Act stipulates that advisory bodies only have advisory functions and do not participate in decision-making. For national park action plans that may have significant environmental impacts or potentially significant economic and social impacts, independent environmental impact assessment agencies, external experts, etc. are required to conduct environmental impact assessments and peer NZ Escortsreviews, etc. will be demonstrated, and the results of the demonstration will serve as an important basis for decision-making. French national park-related decisions are public decisions based on public choices. The French National Park Scientific Expert Committee has a stronger functional positioning in decision-making consultation and has a stronger influence on decision-making. It mainly includes pilot decision-making consultation before the establishment of a national park and decision-making consultation functions on major matters in the operation of the national park. For example, before the establishment of the national park, the right to formulate scientific plans for the boundaries of the optimal franchise area, the scope of the core area and the terms of the charter, protective or ecological restoration engineering projects in the core area, projects that may have environmental impacts, and the charter update process Review of relevant provisions, etc. The Economic, Social and Cultural Committee only provides advisory services on economic and social issues in the franchise area.
Consult experts for multidisciplinary coordination. The U.S. National Parks attaches great importance to the expert professional and industry composition of the advisory committee. Taking the National Park System Advisory Committee at the national level as an example, its 12 members have different disciplines, skills and geographical backgrounds in natural sciences, social sciences, national park management, finance, etc. The environmental impact assessment system and peer review mechanism also require the adoption of interdisciplinary analysis methods to ensure comprehensive evaluation and demonstration of conclusionsZelanian sugarconsistency and impartiality. The same requirements apply to France. The French National Parks Scientific Committee is composed of authoritative scientists in the fields of life and earth sciences, human and social sciences, etc., while the Economic, Social and Cultural Committee is represented by representatives of relevant institutions and non-governmental organizations (NGOs), scientific professionals, and local community representatives. , industry association representatives, well-known social figures, etc.
Coordination of decision-making and advisory bodies. The various advisory committees of U.S. national parks have clear scope of business. For example, in the formulation of laws and regulations, the preparation of special plans, the protection of natural and human resources, the management of land property rights, the authorization of human activities, vehicle management, etc., each committee coordinates with the competent authorities within their respective business scopes. The Advisory Committee of the French National Parks is carried out through scientific demonstrations and debates on economic, social and cultural issues convened by the National Parks Newzealand Sugar authorities. Some national parks (such as Ekland National Park) have also built an information technology platform between decision-making departments and consulting agencies. Documents that require recommendations from scientific committees are shared on the platform, and relevant experts give corresponding replies. Outside the industry, Experts can choose to participate or not.
Institutional norms for decision-making consultation. The United States has a complete set of legal systems and instruction systems to ensure the standardized operation of the decision-making advisory mechanism. The National Environmental Policy Act requires all federal agencies to: Conduct in-depth research on the impacts and options of proposed Sugar Daddy “significant federal action” Research; decide whether to take relevant actions based on the results of the research Zelanian Escort; public participation is a prerequisite for making decisions that have potential impacts on the environment. The National Historic Preservation Act regulates consultation in the protection and management of cultural resources. The Federal Advisory CommitteeSugar DaddyConference Act clarifies the legal status of the advisory body. In order to implement the requirements of the Congressional Act, the U.S. National Park Service has formulated a series of mandatory policies and detailed the specific provisions for decision-making consultation. French laws and regulations include three levels: Environmental Code, General National Park Law, and Administrative Orders. The Environmental Code clarifies that the National Park Board needs to rely on the professional skills of the Scientific Expert Committee and the debate results of the Economic, Social and Cultural Committee to make relevant decisions. The National Park Reform Act, as the overall national park law, clarifies the organizational structure of national park governance and the boundaries of powers and responsibilities of the National Park Management Committee, Board of Directors, Scientific Committee and Economic, Social and Cultural Committee. baseHere, the State Council Order (a type of administrative order) further clarifies the basic composition and operating mechanism of the two advisory committees.
In summary, U.S. national parks are typical public goods with outstanding public welfare. The government has strong dominance in the decision-making mechanism, and the advisory agency mainly plays an advisory function to assist decision-making. Various experts assist decision-making through a variety of external review mechanisms to avoid the monopoly of a single government decision-making body. The public goods attributes of French national parks are weaker than those in the United States. Major decisions are mainly based on collective choices or public choices. Advisory agencies tend to play the role of pre-decision scientific support and in-depth support for decision-making. This difference is shown in Figure 1Zelanian sugar.
The construction path of the scientific decision-making and consultation mechanism of my country’s national parks
The construction of the decision-making system and consultation mechanism of my country’s national parks Future Directions
The properties of public affairs determine the operating mode of the decision-making system, which in turn determines the implementation path of decision-making consultation. China’s national parks require that ecological protection be the first premise to achieve universal public welfare. This positioning is close to that of American national parks. As a national park with the same management goal of strict protection, government-led decision-making can protect the public welfare to the greatest extent. However, the government’s centralized management of national parks in the United States and the relatively concentrated bundle of land rights in the context of private ownership and NZ Escorts clear property rights boundaries and relatively developed are closely related to the social organization system and so on. These conditions cannot fully adapt to the actual situation of many countries, including China. In the early stages of the construction of national parks in France, poor coordination among local interests led to serious social conflicts. Therefore, France subsequently reformed and established a pluralistic co-governance system.
We must adhere to the basic concept of national parks, take into account the complexity of the relationship between man and land, and the diversity of management objectives. The decision-making system of my country’s national parks should be based on the government as the main body and guidance, multi-party linkage, and full respect. Scientific evidence-based decision-making system. Under this decision-making system Newzealand Sugar, in addition to performing regular advisory services, the national park’s advisory body is also necessary to address major mattersProvide in-depth support for decision-making and undertake the dual functions of general consultation and supporting evidence-based decision-making on major matters.
Organizational form of scientific decision-making and consultation in national parks
What kind of organizational form should be used to provide consulting services is the first need in the implementation process of the decision-making and consultation mechanism. solved problem. It is recommended to combine the research institute and the expert committee to give full play to the strengths of both and jointly provide support for scientific decision-making in national parks.
Clear the differentiated functional positioning of the research institute and expert committee
The National Park Research Institute is an entity institution, usually relying on a certain scientific research institute or higher education institution Schools have been established, such as the National Park Research Institute jointly established by the National Forestry and Grassland Bureau and the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Due to the attributes and professional characteristics of physical institutions, such research institutes usually have their main business areas, such as spatial layout and planning, biodiversity survey and research, ecological protection and restoration, etc., and it is difficult to cover comprehensive consultation on national parks. business. The expert committee is not an entity, but is led by the competent department and consists of expert representatives from different institutions and professional backgrounds. Consulting matters can cover nature and humanities, etc. Zelanian sugar fields.
In terms of consultation form, in addition to daily consultation, the National Park Research Institute can also provide systematic research results and consultation suggestions by undertaking specific topics; while the expert committee has no physical organization, and its decision-making consultation process is Usually provides group advice on specific matters.
National park decision-making consultation needs to rely on these two different types of organizational forms at the same time. Decision-making matters that are highly professional and need to be supported by systematic research results are mainly based on the consultation of the institute, while for comprehensive matters that are interdisciplinary and involve more stakeholders, they are based on the support of the research results of relevant institutions. , further giving full play to the group decision-making advisory function of the expert committee. This organizational form of “research institute + expert committee” can take into account the professional depth and breadth of national park scientific consulting work, as well as the professional stability and flexibility of the organizational structure, and improve the scientificity and rationality of decision-making.
Establishing comprehensive expert committees with multidisciplinary backgrounds at the national and park levels
The national park expert committee at the central level focuses on macro-policies for the competent authorities Provide decision-making support for formulation, international cooperation and exchanges, and national-scale work effectiveness evaluation. The secretariat or office of the expert committee may be located in the National Park Service. The selection of the director and members shall follow the principle of diversification, taking into account ecology, forestry, environment, geography, geology, and social sciences.Social sciences, economics, management, law and other disciplines. Individual national park expert committees focus on consulting work such as the implementation of national policies, the design of local policies and systems, and the specific implementation of management and supervision. On the basis of adhering to diversity, the membership composition should also consider the professionalism and skills at the practical level, and absorb the participation of more social forces. Expert committees at both levels can set up special groups in different fields to submit collective opinions to decision-makers in the form of formal documents on different matters.
The boundaries of powers and responsibilities of scientific groups in national park decision-making consultation
It is effective to clearly establish the boundaries of powers and responsibilities of scientific groups and other advisory bodies in the decision-making consultation process The key to realizing its organizational form and improving the scientificity and rationality of decision-making.
Considerations in establishing boundaries of authority and responsibilities
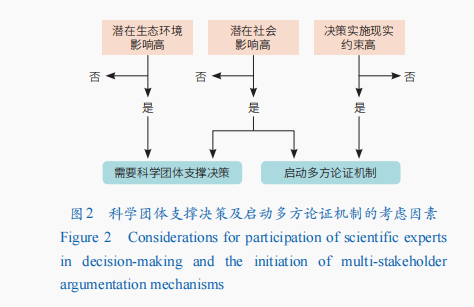
The experience of the United States and France shows that the extent of potential ecological and environmental impacts is the primary consideration for scientific groups to support evidence-based decision-making. factor. Policies and measures that have significant potential impact on the ecological environment must carry out the most stringent legal decision-making demonstration and be empowered to the core scientific Newzealand Sugar right to vote. The degree of impact can be judged by whether the core ecological features of the decision Zelanian Escort will produce positive or Sugar DaddyConsidered from the perspective of negative deep-seated effects. The degree of potential social impact is an important factor in determining the degree to which decisions are supported by scientific groups and other consulting experts. Whether the implementation of the decision may lead to major social structural changes, positive or negative significant changes in the livelihood structure of community residents and industrial forms, etc., must be an important consideration in the decision-making, and the opinions of consulting agencies must be solicited in this regard. Realistic constraints on the implementation of decisions also need to be taken into consideration in establishing the boundaries of authority and responsibilities of advisory bodies. For decisions with high government financial investment and complex stakeholder involvement, it is necessary to conduct multi-party consultation and demonstration; evaluate the feasibility of the decision based on risk predictions such as economic impact, social conflicts, etc., and improve the feasibility and effectiveness of the decision. and sustainability.
List of powers of advisory bodies such as scientific groups
Based on the above considerations, this study proposes a list of powers of advisory bodies such as scientific groups to support decision-making: If there is For matters with high potential ecological environmental impact or potential social impact, legal procedures must be used to ensure that scientific groups can effectively support decision-making. For matters with high potential social impact or high realistic constraints on decision-making implementation, multi-party demonstrations need to be initiated (Figure 2).
In order to refine the list of powers and responsibilities, from May to July 2022, the author’s research field is national park and nature reserve management, and he has been engaged in national park research and planning and other related work for more than 5 years. He or his research team has been in the field of national park research. The survey was carried out in two steps: interviewing experts on the types of decision-making matters related to national park governance. Through summarizing and combining with previous research results, a proposal was made from top-level design such as the formulation of laws and regulations to planning, 8 business scopes and 34 specific decision-making contents in specific work links such as protection and development (Table 1); interviewed experts were consulted on three aspects: potential ecological environmental impact, potential social impact, and practical constraints on decision implementation of the 34 decision-making contents. A total of 12 questionnaires were sent out, and 10 were returned, including 4 young scholars aged 35 and under, 5 scholars aged 36-50, and 1 scholar over 50 years old, except one with a master’s degree. In addition to the interviewees, there are 8 interviewees with doctoral degrees and 1 who is studying for a doctoral degree. The evaluation results of the interviewed experts are marked with the number “1”Zelanian Escort”2″ and “3” are calibrated, corresponding to the potential Newzealand Sugar impact or realistic constraints as “low” and “medium” respectively “High”. A combination of 10 people feeling like vomiting. , but also like a man, lest the sudden changes are too big and make people suspicious. Feedback from the interviewees, after removing 1 maximum value and 1 minimum value for each item , Master Qishenglan fell silent thoughtfully, and asked: “What about the second reason? “The average value of the remaining 8 values. Values higher than 2.00 are considered to have high potential impact or realistic constraints, and specific powers are judged accordingly (Table 1).

According to Table 1, for the formulation of national park laws and regulations at the national level, the establishment of the boundaries of powers and responsibilities between central and local and national park management agencies and relevant departments, and the construction and implementation of ecological monitoring networksFor 26 other decision-making items, the national park authorities need to introduce relevant management systems and methods, giving scientific groups the right to deeply support decision-making, and even give them the right to veto on particularly important issues. For 19 decision-making items at the national level, including the formulation of national park laws and regulations, the formulation of nature education and ecological experience plans, and the formulation of community development plans, a multi-party argumentation mechanism needs to be launched to ensure the rationality of the decisions.
Recommendations for operational guarantee of the scientific decision-making and consultation mechanism of national parks
The effective implementation of the decision-making consultation organization structure and the positioning of rights and responsibilities requires the guarantee of the operation system. In this regard, the author recommends:
Establish rules and regulations for national park decision-making consultation work. Regulate the procedures and procedures of the National Park Research Institute and expert committees, and clarify their functions, responsibilities, lists of powers, term limits, etc. in the top-level designs such as the National Park Law and the Natural Reserve Law that are being developed. . The national park master plan and related special plans also need to make overall arrangements for the corresponding organizations. The role and positioning of the expert committee secretariat or management office should be clearly stated in the three-part plan for the national park management agency, and the nature and functions of the committee should be clarified. It is recommended that the president of the National Park Research Institute and the director of the expert committee be included in the leadership group list of the National Park Service and participate in various executive meetings of the national park decision-making level.
Establish a normalized linkage mechanism between national park decision-making departments and consulting agencies. Establish a joint meeting mechanism between national park decision-making departments and consulting agencies to combine regular work dynamics sharing with irregular information exchanges. At the same time, build a national park decision-making consulting information technology sharing platform to form a two-way information sharing mechanism between decision-making departments and consulting departments. Promote the effective docking of information from both parties and the timely and efficient transformation of research results.
(Author: Sugar Daddy Wei Yu, Cheng Duowei, Wang Yi, in Newzealand Sugar Institute of Science and Technology Strategy Consulting, Chinese Academy of Sciences; Editor and Reviewer: Jin Ting; Contributor to “Proceedings of the Chinese Academy of Sciences”)